Barbaros Mh. Sıra Perde Sk. No: 17/1 Üsküdar / İSTANBUL / Türkiye
About Lead
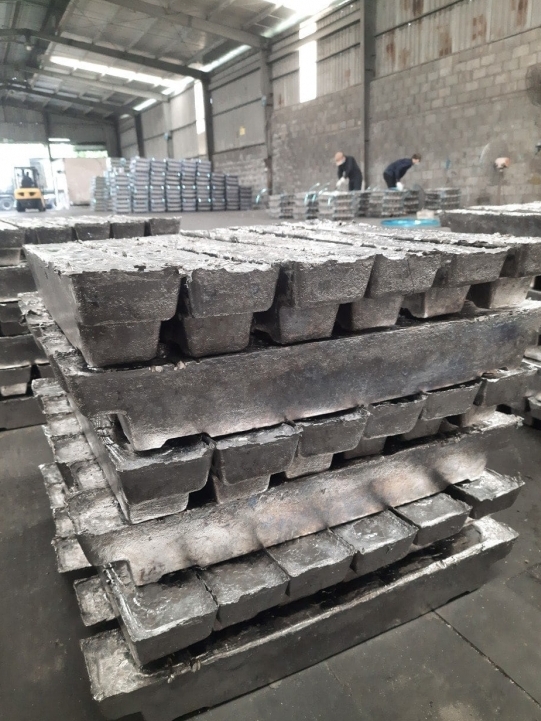

What is Lead?
Lead (Pb) is a blue-silver mixture element with atomic number 82 and atomic mass 207.19. It melts at 327.5 °C and boils at 1740 °C. Its frequency in the earth's crust is 12.5 g/t. It is among the metals that can be found naturally. It is one of the oldest metals in use. Alchemists describe lead as the oldest metal. It is known that lead was first used in a figure from 3000 BC found in the ancient city of Abidos (Abydos).
Physical Properties
Lead is a soft gray metal. It is both ductile and malleable. Its surface is glossy in its first production, and gradually darkens and becomes dull over the years. Lead is an easily machinable element. Thanks to its machinability, its shape can be changed easily and it has a structure that can be used as desired. Lead has a melting point of 327.4°C and a boiling point of 1,750°C. Its density is 11.34 grams per cubic centimeter. Lead does not conduct electricity, sound and vibration very well.
Chemical properties
Lead is a moderately active metal. It dissolves slowly in water and most cold acids. Reacts faster with hot acids. It does not react immediately with oxygen in the air and does not burn.
Uses of Lead and Production Process
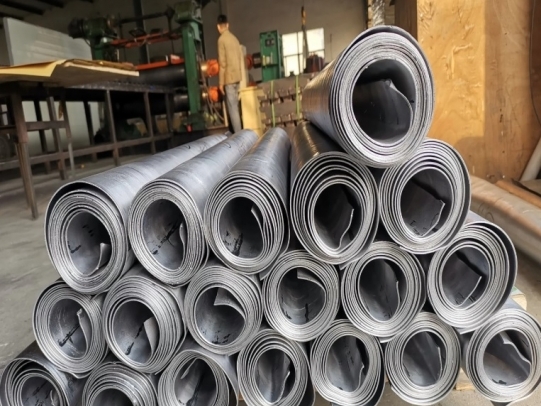
Since lead is an easily machinable and corrosion resistant metal, it has been used in pipe making, tinning and paint since Roman times. It is also used as lead glaze in the pottery industry, in pesticides, hair dyes and as an anti-knock additive for gasoline. It is still widely used in many areas today due to its being a common metal and its low melting point (327.5 °C).
The main areas of lead use today;
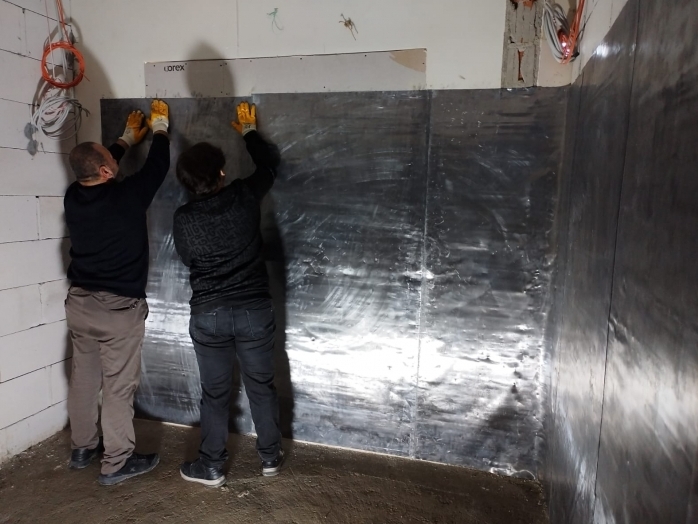
Radiation Insulations
Mosque Dome Coverings
Historic Building Restorations
Battery Production
Ammunition Making
Chemicals and pigments
Gasoline contribution
Sound Insulation
No comments yet, be the first to leave a reply





Comments (0)